A strong sender reputation is the basis of optimum email deliverability and competent email performance. Sender reputation is determined based on the perception of your mailbox providers and subscriber engagement. In other words, if people engage with your emails and fetch you a higher click-through rate, you will have a strong sender reputation. Contrarily, if people don’t open your emails, unsubscribe, and mark them as spam, it will have a negative effect on your sender reputation.
Surprisingly, your sender reputation will be variable across all mailbox providers. It’s not an absolute value. An Internet Service Provider (ISP) gives you a score by weighing down your email sending behavior and evaluating the conformance to ISP’s guidelines. It considers complex statistics to reach this score. Email sender reputation is a combined figure obtained from IP and domain reputation.
To start with, let’s understand IP reputation and domain reputation, and then the differences between the two.
What is IP Reputation?
An IP address is a unique number used to recognize computers on the Internet. It serves as an address used by other computers to search for your computer. While sending an email, ESPs use the IP address linked to your sending domain to figure out the source of the email.
IP reputation refers to the IP address through which the emails are deployed. It helps determine if email servers can receive emails that are sent for the particular address. There are two types of IP address you can use:
1. Dedicated IP address
2. Shared IP address
In case of dedicated IPs, you don’t have to worry about the other senders. The IP reputation will be in accordance with your email sending habits. Contrary to this, if you are using a shared IP, the sender reputation will be a reflection of how everyone using it is sending emails. Unfortunately, some mailbox providers are unforgiving and they blacklist you even if the spammy email is done by someone else using your shared IP.
Interestingly, you can reset the IP reputation by updating the domain’s IP address.
What is Domain Reputation?
A domain is the name given to your sending email server. Email servers use it to find your IP address. Domain reputation is the rank of your email sending domain, determined by your past email sending patterns and the engagement rate. You cannot reset the domain reputation as it is linked to the domain name. So, domain reputation can be considered somewhat indelible in comparison to IP reputation.
You have to consider three types of domains for email sending.
a. From Address
b. Return-Path domain
c. DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM)
All these three domains influence the domain reputation. Therefore, you must manage them well if you want to improve your domain reputation.
Calculating Email Domain Reputation
Just like you have a credit score according to your spending habits, you have email domain reputation according to your email sending habits. Wow, that rhymed!
ISPs take the help of complex, secret algorithms to score a domain from 0 to 100.
The higher your score, the more trustworthy your emails are.
They keep a tab of the domain’s usage in an email and how the email looks in the inbox. Also, they authenticate the score while scanning the future emails.
The good news is that we have figured out the parameters considered by Email Service Providers to calculate domain reputation.
They are:
1. Spam placement rate
2. Email forwarding rate
3. Spam complaint rate
4. “Marked as not spam” rate
5. Read rate
6. Deleted for reading rate
7. Open rate
8. Click rate
9. Reply rate
10. Hard bounces
11. Spam traps
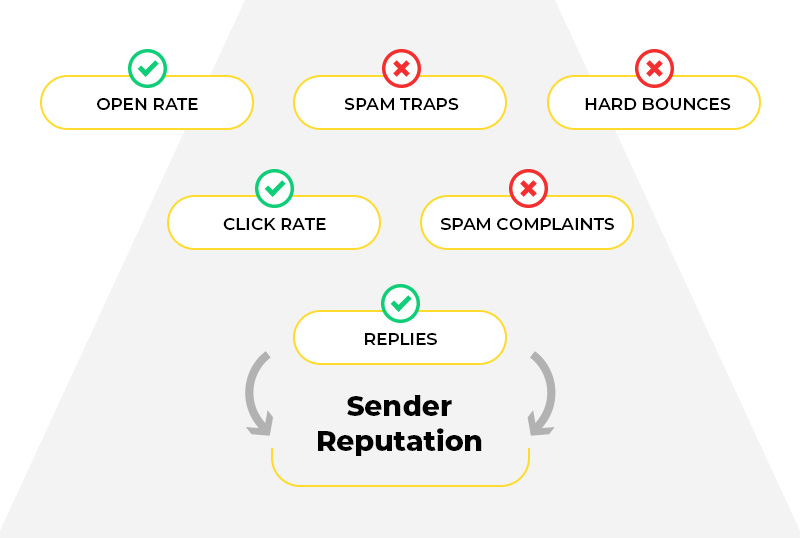
All these parameters count and make a difference to your domain reputation. The email recipient behavior governs these factors. So, it will be a challenge to rectify a low domain reputation. It hurts to write this but even your transactional emails will go to the spam folder. Your email strategy will make almost no sense if you have a bad domain reputation.
So, how will you check your reputation score?
Tools to Assess Email Sender Reputation
I am sure you are curious to know how to improve your sender reputation and what to do if it goes for a toss. We shall discuss it but before that here are some tools that will let you check email domain reputation.
1. SenderScore.org
Validity provides free email reputation evaluation service. The Sender Score shows you the reliability of the email sender’s IP address. It is a score given from 0 to 100. A higher email reputation score reflects better email sender reputation and an optimum deliverability rate. It is calculated considering a 30-day average and reflects how your IP address performs in comparison to the other IP addresses.
2. BarracudaCentral
BarracudaCentral allows you to learn about your IP as well as domain reputation. The email reputation service uses a real-time database to sort the IP addresses into good or bad. It evaluates the sending history associated with the IP addresses of all the sending mail servers. This helps identify the likelihood of authentic communications deployed through the addresses. Accordingly, the Barracuda Spam and Virus Firewall will deny or enable the email, considering the sender’s IP address.
3. MxToolbox
MxToolbox informs you about who is sending email through your domain, their IP’s reputation, and location. It will also let you know about the problems with your domain, based on Blacklists, Web Server, DNS, and Mailserver. In case there’s a variation in the email reputation, the system will immediately update you.
You can either go for the free version or the paid package. The free version includes a single blacklist monitor and weekly blacklist monitoring. The premium versions start at USD 129 per month. You get dedicated expert support and regular email delivery performance reports along with several other useful features. If you are looking for advanced email delivery threat tools and SPF flattening features, the plan starts at USD 399 per month.
4. Google Postmaster Tools
Google offers enormous data on the delivery rate of emails. It uses Google Postmaster Tools to reveal how they interpret certain domains on receiving an email from them. They offer information about the IP reputation, domain reputation, Gmail delivery issues, and several other details like spam reports, email encryption, and authentication.
5. MailTester
If you are looking for a complete report on your content, mail server, and sender IP address, MailTester is the best tool for you. It is an affordable way to check mail server reputation online. The free version of MailTester gives access to the results for seven days while the paid one allows you to keep the results for 30 days.
6. Ipvoid
APIVoid’s Domain Reputation API created Ipvoid, which assesses your domain reputation by comparing the IP address with blacklisting engines. A number of popular domain blacklists like ThreatLog, PhishTank, OpenPhish, etc. will notify you in case a domain name is put in the malicious or phishing list. For people looking for instant analysis of their domain, Ipvoid is the safest bet for you.
With an insight into the tools to measure the email sender reputation, we shall now shed light on how to improve it.
5 Tips to Improve Your Sender Reputation
1. Warm up your IP address
When you get a new IP address, it has no sender reputation. The modus operandi of malicious agents is to keep switching IP addresses to bypass spam filters and blacklists. If you start sending mass emails from a new IP address, the ESPs and ISPs will consider it as spammy behavior.
So, as a best practice, you should slowly increase your email send volume over around 15 days. You can send out 100 emails initially and then increase the number till you reach the number of your subscribers.
If this isn’t your forte, you can avail email marketing management services from Email Uplers.
2. Set up email authentication protocols
Email authentication protocols let the email servers know that your emails are genuine. If you need help with setting them up, you can approach an email marketing agency for the same.
a. SPF
SPF verifies that the email sender is genuine and who they are claiming to be. It keeps the email recipients safe from malicious intentions.
b. DKIM
DKIM authentication protocol prevents any alteration of the email during the transit. It protects people from man-in-the-middle attacks and malicious agents who swap the emails when they transition to the subscriber.
c. DMARC
DMARC authentication lets the receiving mail servers know the authentication process of your emails. So, the mailbox providers get an idea about the authentication protocols that should be mentioned. In case of a missing authentication standard, mail servers will be warned that the email is not from you.
3. Maintain a proper list hygiene
Regular pruning of your email lists is imperative if you want to have a good deliverability rate. Remove any invalid email addresses or email ids with typos as they have a negative effect on your deliverability rate. Try to re-engage the dormant email subscribers and remove them if they don’t respond even after a series of 2 or 3 winback emails.
4. Take a double opt-in approach to build the email list
A double opt-in method will help ensure that your email list gets subscribers who are genuinely interested in hearing from you. It will also reduce the unsubscribes, thereby maintaining your deliverability rate.
5. Craft relevant and personalized emails
Send valuable content in your emails that will compel the users to read till the end and even forward it. Personalize them according to the user’s preferences and buying behavior. You can also incorporate attractive visuals and interactivity to encourage more subscribers to engage with it. In addition, go for an email template audit and incorporate the suggested changes.
Now, suppose you check the reputation score and get a score of 40. So, how will you improve it?
We have your back. Here are some easy and actionable tips to help you.
1. Check the feedback loops
Feedback loops will let you know whether you have a good or bad sender reputation. You will be able to see a feedback header in the email provider. It will give you detailed insights into the deliverability issues. Based on that, you can resolve the problems and stop sending emails that negatively influence your sender reputation.
2. Invest in a subdomain for sending email
Having an exclusive subdomain will make your subscribers identify your brand and mark your emails as not spam in case they land in the spam folder. Moreover, it is worth investing in a dedicated IP address so that your sender reputation is not influenced by others.
3. At the outset, use the email subdomain to send transactional emails exclusively
As transactional emails have a high open rate and click-through rate, they will contribute to building a good sender reputation. When you are just starting off, use the subdomain to send only transactional emails. Once your subscribers start marking your emails as not spam and your email reputation improves, you can send promotional emails from the subdomain. Subsequently, get a new IP address for sending the transactional emails. Follow the warm up strategy as mentioned earlier in the article.
4. Keep an eye on the number of emails you send
You will need to send more than 100 emails per day to get noticed and build the sender reputation. Your email cadence is a crucial parameter impacting sender reputation. So, avoid sending too many emails if you want to eliminate sending any negative signals to ESPs.
Wrapping Up
High email deliverability → Better sender reputation → More profitable email campaigns
If your emails are not performing according to your expectations, there is a possibility that your IP address or domain is blacklisted. Note that you won’t be notified if your domain name IP gets blacklisted. So, you must monitor the blacklist database services and use the tools stated in the previous section.
And if you are still unsure how to go about it, get in touch with an expert and seek help.



Disha Bhatt (Dave)
Latest posts by Disha Bhatt (Dave) (see all)
6 Factors to Consider While Hiring Dedicated Email Resources
10 PPC Landing Page Best Practices Every Marketer Must Know (with examples)